How Does Night Vision Work: A Quick And Simple Guide
First, have you ever heard of the saying, “What you do not see cannot hurt you?” Forget that! What you do not see can, and most likely will, hurt you.
In America alone, 71% of pedestrian accidents happen at night. Improved night vision would slice the number by half. Such are the statistics that have popularized enhanced night vision. But, exactly how does night vision work?
This question does not have a single answer.
Different Night Vision Devices (NVDs) operate under different technologies. To answer this question, we must look at the different techniques.
There are two leading Night Vision Enhancement technologies:
- 1. Thermal Imaging
- 2. Image Enhancement

Image Enhancement
As dark as it may seem, there is always light. It is in fact practically impossible to get rid of all light. Such a feat is only possible when using specialized equipment. It also has to be done under strict laboratory conditions.
Not all light, however, is visible to the naked human eye.
This invisibility is what makes moonless nights seem so dark. Ultra Violet light (UV) and Infra Red (IR) lights are invisible spectrums of light. The interesting thing is that they work just like visible light.
They still bounce off objects and into our eyes. The problem is that we cannot process such spectrums. We are, therefore, blind to the images they bring to our eyes.
Some reptiles, however, have natural IR receptors. These IR sensitive cells allow them to see in the dark.
Humankind is a step ahead of animals. What we do is adapt the environment to fit us.
Humankind has developed NVDs that can detect such light. They then amplify it and convert. Our naked eyes can then process the converted light.
That explains Image Enhancement Technology in a nutshell. Capturing all light bouncing off objects and amplifying it.
Image Enhancement Technology (IET) is also known as Image Intensifying Technology (IIT). Night vision goggles and cameras employ the technology extensively. Let us look at the two NVDs more closely.
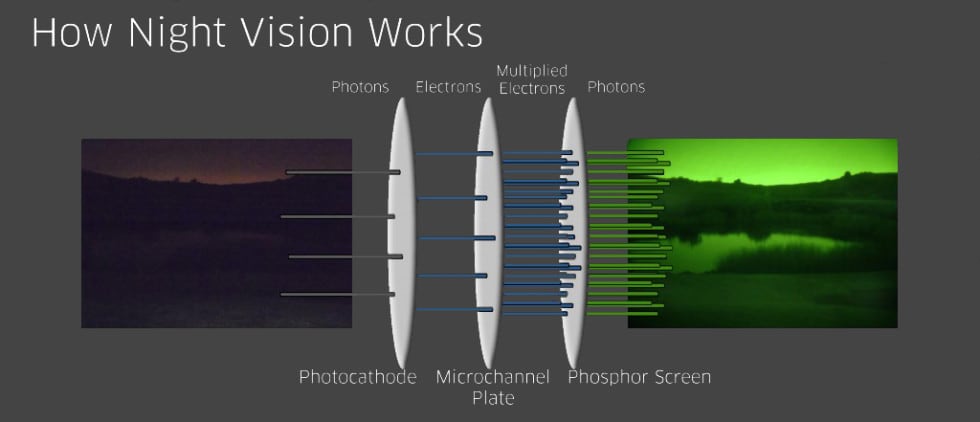
Image Credit : http://nightvisionhome.com/
How Does A Night Vision Camera Work?
Look closely at a night vision camera. You will notice it has many LED bulbs. These bulbs are the Camera’s source of IR light.
The bulbs blast Infra Red rays towards the camera’s field of view. This IR blast, however, only happens at night.
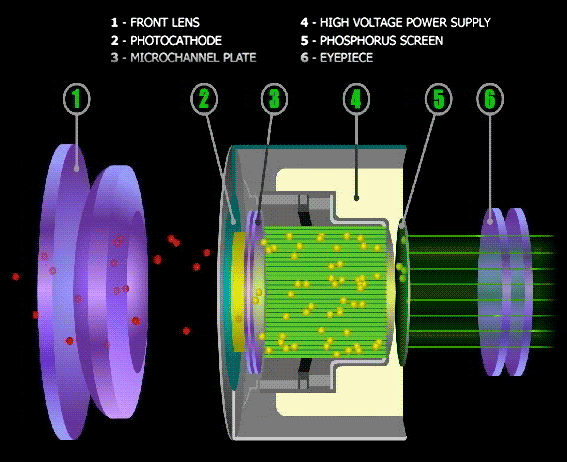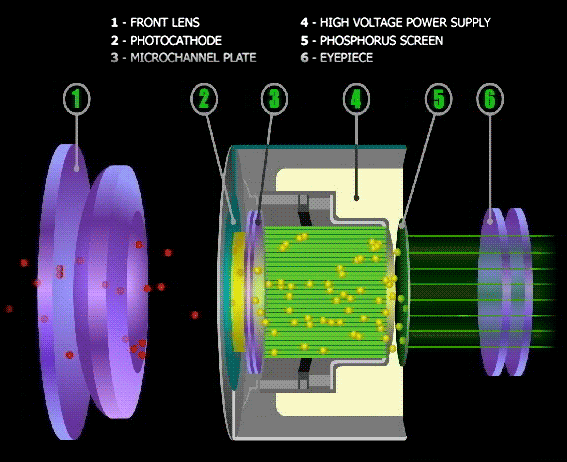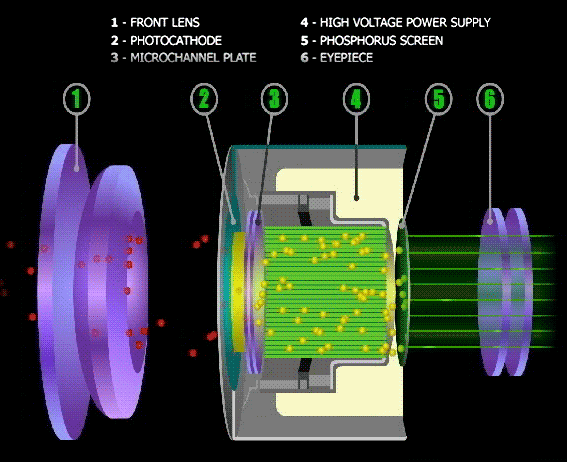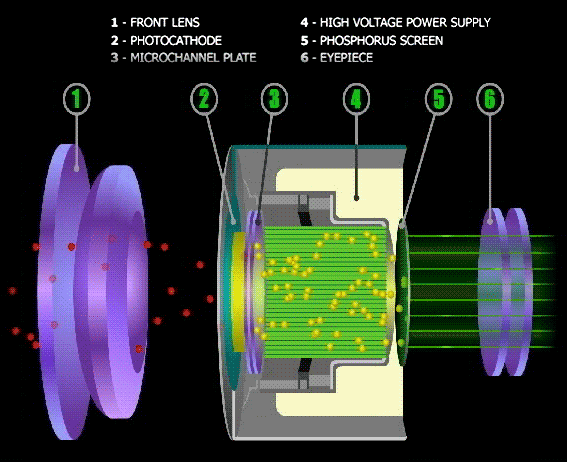
Image Credit : https://www.atncorp.com/
If IR were visible to the naked eye, the whole place would be bright red. Now, this raises a fascinating question. If Infra Red is RED, why is the footage from security cameras always black and white?
The answer is simple. While processing the IR images, Night Vision Cameras use Monochromatic filters. Monochromatic filtration is the black and white development of imagery by Cameras.
Why would it be preferable to create black and white imaging to colored imagery?
Now the answer to this is absorbing.
Black and white imaging is best for security cameras. The notion goes against popular belief but is true.
Humans will more easily distinguish black and white than any other color hues. A moving object will, therefore, be noticed faster under Monochromatic conditions.
N.B.: Monochromatic is just a fancy name for black and white.
During the daytime, the IR feed terminates. An inbuilt IR cut filter handles this termination. It cuts off the IR LEDs when it detects sunlight. That is how a night vision camera works, in a nutshell.
--- Let us now jump to IR Night Vision Goggles 🙂
How Do Infrared Night Vision Goggles Work?
Image Enhancement is slightly different in Night Vision Goggles.
Night Vision Goggles employ devices called Intensifier Tubes. As the name suggests, they intensify light that passes through them.
So how do you amplify light?
The answer is again very simple. YOU DON’T!
Electric signals are the only things we can intensify directly. The trick, therefore, is to convert light into electrical signals. The signals can then be amplified and re-converted back to light.
Voila, you have intensified light! 😀
Black and white imaging is best for security cameras. The notion goes against popular belief but is true.
The Intensifier tube converts received light (photons) into electrons (Electric signals). A photomultiplier then amplifies the signals.
The amplified electric signals are then blasted onto the goggles phosphorous screen. The screen converts the signals back to the light.
The result is a far brighter image observed through the goggles. Light from objects enters the binoculars bearing all colors. The image is, however, always green.
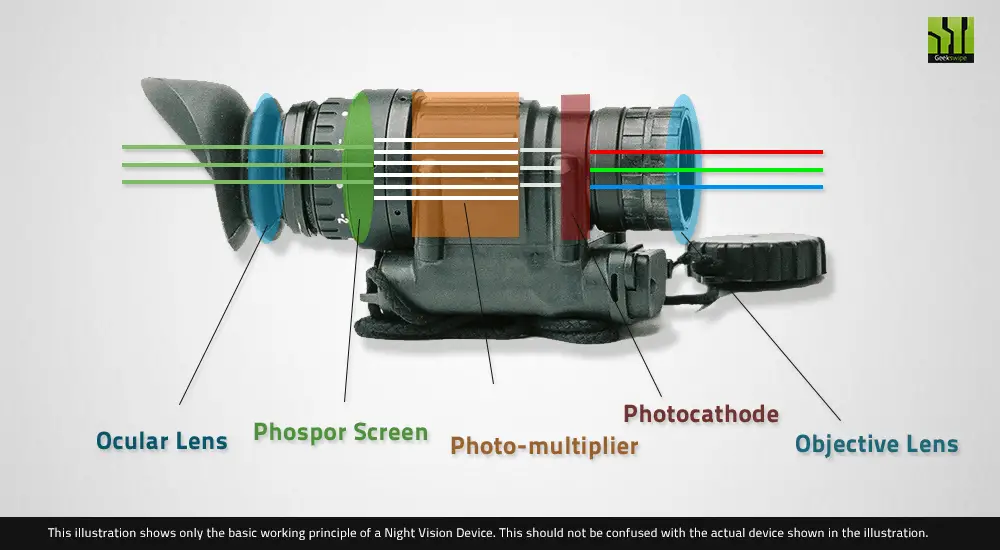
Image Credit: https://geekswipe.net/technology/electronics/how-night-vision-systems-work/
Why are images from night vision goggles always green?
Again, the green is by design. A design much like the IR Camera’s black and white images.
Human eyes are most sensitive to green light. It is also easier to look at green images for extended periods of time without fatigue.
Such goggles were developed for military use. It was, therefore, important that a soldier remained comfortable for long.
Now, that answers, ”How does a night vision binoculars work?”
N.B.: Night Vision Goggles are just Night Vision Binoculars with headgear.
Image Enhancement Technology works on the premise of amplifying available light. The technology is useless in 'true darkness.' As stated earlier, however, a 'light-absent' environment is difficult to achieve.
What most people wonder is if the night can ever be too dark for Night vision goggles.
So, do night vision goggles work in complete darkness? NO. They cannot operate in 'true darkness.' The night can, however, never be too dark for operation. Even the darkest of nights has a lot of invisible light.
Image Enhancement Technology (IET) has its strengths and weaknesses.
Strengths
- Identification of people is possible
- Sensitivity to low-light is splendid in this NVDs
- Overall performance is better than Thermal Imaging
- Low power consumption
- The technology is relatively cheap to implement
- The overall cost of such NVDs is cheaper than their Thermal Imaging counterparts
Weaknesses
- These NVDs are potentially harmful to eyes when used under intense light
- Cannot work in 'true darkness.
- Daytime performance is less than satisfactory
Thermal Imaging
Image Enhancement Technology (IET) utilizes light bouncing off from objects. The light can be naturally occurring or shot from the NVD. NVDs that shoot their light always outperform those that do not.

For purposes of discretion, however, the light from such NVDs is usually invisible to the naked eye.
Most Night Vision Binoculars on the market have LED bulbs between their two scopes. The Technology is easy to use and cheap to implement. These conveniences have made it very popular.
Let us now give an in-depth look to Thermal Imaging.
Unlike Image Enhancement, Thermal Imaging utilizes heat and cold signals from objects.
You need to understand that light has a very broad spectrum. Visible light, light visible to the naked eye, is just part of it. Infra Red is an invisible spectrum relevant to Thermal Imaging.
Bodies radiate heat signals in the form of IR light. Thermal Imaging NVDs process such signals. The greatest misconception of this technology is that it works like X-rays.
This is false!
X-rays can see through walls but thermal imaging cannot. Thermal imaging can only show inside, but not beyond, the wall. To understand this concept, remember how heat is transferred.
In solids, it moves by conduction. Conduction implies that parts of the solid are heated and heat consequent parts. The repetition of this process transmits the heat energy across the solid.
When a wall conducts heat signals from objects behind it, it alters them. The alteration makes it impossible for thermal imaging to detect objects behind walls.
So, how does thermal imaging REALLY work?
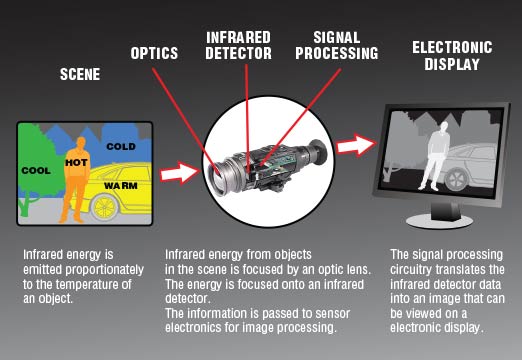
Image Credit : https://www.atncorp.com/howthermalimagingworks
- i. For starters, heat escapes from bodies in the form of Infra-Red rays. A special kind of lens receives the IR rays from its field of view.
- ii. The IR rays are focused into the Thermal Imaging NVD.
- iii. The IR is scanned by IR detecting elements in the NVD.
- iv. The IR detecting elements then create a THERMOGRAM. A thermogram is a detailed temperature image or pattern.
- v. The thermogram is then converted into electric signals.
- vi. An inbuilt signal processing unit processes the signals into data that can be displayed.
- vii. The signal processing unit then sends the signal to the displaying device.
- viii. The displayed signal is an image with different color patches. The color spots represent differing heat signals.
A famous Thermal Imaging NVD is the Thermal Image Camera.
How does a Thermal Image Camera Work?
To answer this comprehensively, we will look at the two types of Thermal Image Cameras.
- Cooled-Detectors Thermal Imaging Cameras
- Uncooled-Detectors Thermal Imaging Cameras
How Cooled-Detector Thermal Imaging Cameras Work?
These Cameras are cryogenically frozen and sealed in vacuums. This lowered temperature translates to increased sensitivity.
The heat signals from these rigs do not interfere with their IR detecting elements.
Thermograms from these cameras are, therefore, very detailed and accurate.
Let us look at its perks and shortcomings
Advantage & Disadvantage of Cooled-Detector Thermal Imaging Cameras
Advantages
- Acute Thermal Sensitivity
- Have massive detection ranges
- Unhindered by bright light
- These cameras can image objects moving at high velocities
- Can be used for multi-spectral IR imaging
Disadvantages
- The coolers limit the cameras operating life
- Very expensive
- Very bulky
- Initiation is slow as it has to cool down before use.
How Uncooled Thermal Imaging Cameras Work?
These cameras operate at room temperatures. A baseline signal is first developed at rest (room temperature). IR detecting materials convert incoming IR into electric signals. These signals are contrasted to the baseline signal. A thermogram is then created from the comparison.
Advantages
- Easy identification of big objects like vehicles and animals
- Relatively cheap
- More reliable than their cooled-detector counterparts
- Enjoys excellent contrasts
- Unaffected by light
Disadvantages
- Less sensitive than Cooled-Detector Cameras
- Cannot image objects at high velocities
- Cannot be used for multi-spectral imaging.
All in all, Image Enhancement Technology (IET) is more common than Thermal imaging. IET allows for portable NVDs. Portability is a well-sought aspect of vision enhancement gadgets.
Related: Can You Use Night Vision In Daytime
